Introduction
To set the following discussion into context, my name is ‘Jonny’ Jiang, I am a PhD candidate on service design and service innovation at a design school in London. I am working part time with Paul at a start-up charity Plan Zheroes to deliver services to make better use of surplus food and help people in food poverty.
I am working part time with Paul at a start-up charity Plan Zheroes to deliver services to make better use of surplus food and help people in food poverty.
Thanks to Paul, I have been given opportunities to learn from his expertise in knowledge management and practice some of his methods to capture knowledge and insights in that charity.
As result, I am able to reflect upon my journey of knowledge management at the charity and my research in service design.
Interestingly, by comparing these two distinctive fields of practices, it gives me some thoughts around the importance of how we can generate new knowledge and insight around innovation.
KM tools for learning during and after
Let’s talk about some of the knowledge management methods I learnt in this process. Before jumping into these practices, I should tell you I had very little understanding of knowledge management apart from my general reading around business journals.
Paul sat down and demonstrated to me one of the previous knowledge capture sessions he ran with one of employees at the charity. He explained the rationale of capturing and sharing knowledge among staff through interviews with employees before their leaving and during their life cycle with us.
As I understood, it is very important to understand each individual’s experience and perspectives on his or her journey here and on specific events in particular in order to spot and improve the internal and external operation.
One of the other rationales I understood very well at the end is Paul’s point on the element of constructively building a better relationship with interviewees even after their leaving to help them reflect upon the personal growth and learning during the period of working inside the organisation, which I realise is very important to each party and helps nurture Alumni Networks.
Later on, I have been given an exercise to listen to Paul’s recording on his interview and using his knowledge management toolset (e.g. brief, time map, experience circle, questions) and conclude my findings based on those.
Then a few days after, we sat down again to compare our capture of knowledge based on the same interview and reflected together on some of my questions and learning’s. This was an incredibly effective session with Paul because I am able to learn by practice from Paul’s expertise to help equip a newbie in knowledge management with knowledge, practical tools and confidence.
I took the lessons and tools from this exercise and conducted an interview with employee who was about move to another city and leave the charity. Once the interview has done, I sat down with Paul again to reflect on my interview and report of this knowledge capturing practice.
Most of Paul’s methods have been already described and explained very well in this blog, so if you want to figure out what tools and methods I have used, please click on this post ‘Going not forgotten: knowledge capture in a hurry’.
Check out the timeline tool as a way to effectively reflect the knowledge and insights accumulated along the journey. It is a powerful tool because
- It gives a common language that visually displays our thinking’s and provokes thoughts around the highlights and lowlights of the journey. In my interview it helped us to reflect on interviewee’s expectations at the start of job, which gives us lots of insights on how we manage the expectation during staff induction.
- Mutually, it also gives an opportunity to help the interviewee consolidate the learning from the job that can be transferred to future careers.
My elephant and the correlation between design and knowledge management
As Paul invited me to write down my reflections after this exercise, I was fascinated by how similar and powerful the practices around knowledge management and design as a source for organisational innovation can be. As many of us interpret the word ‘knowledge’ with a connection to ‘science’ ‘scientific’ and ‘objective’, there seems to be a misunderstanding of the value in ‘subjectivity’ and ‘social artefacts’.
As we all come from different experiences in life and become who we are because of those experiences, we all develop very distinctive perspective on the world based on the things we learnt and have done in the past.
It is like one of fables I learnt as a child which described four blind people who gave a very different description of the elephant by touching it from their own positions.
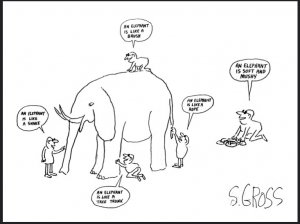 Each seems to be fully convinced by their ‘objective’ interpretation and deny others’ views of what the elephant ‘truly’ is. It is obvious, in the fable, that each of them only ‘sees’ their part of reality.
Each seems to be fully convinced by their ‘objective’ interpretation and deny others’ views of what the elephant ‘truly’ is. It is obvious, in the fable, that each of them only ‘sees’ their part of reality.
The elephant and social facts. source: https://www.flickr.com/photos/climateinteractive/13944682478
In real life, this fable maintains a sense of inspiration too. We all experience a building differently from where we look at it. It can look small from a bird’s eye view or intimidating if standing alongside it.
In organisational management nowadays, particularly large organisations, operations can be highly siloed and lacks ways of detecting those subtleties in perspectives. It means each department may have their very own budget and competing agenda and develop their very own ways of understanding and doing things under the cover of ‘specialisation’.
Those silo operations based on ‘the only one way’ present danger of neglecting the values in perceiving or doing something differently that is at the core of innovation.
As such, knowledge management is becoming increasingly critical to recognise subtlety in each individual’s interpretation and map them in order to spot opportunities in the gap of our personal knowledge and experience.
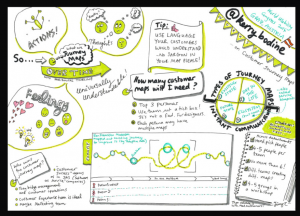 In service design, this idea of interpretation has been very important in user research.
In service design, this idea of interpretation has been very important in user research.
By mapping extensively, designers can understand better the users’ perceptions and behaviours and gather deep insights on where the opportunities can be for designing better customer experience and services.
One example of customer journey mapping. Source: (https://www.flickr.com/photos/97823772@N02/15410073995)
In Knowledge Management these interpretations can often reveal opportunities and strengths as well as failures and weaknesses.
And finally
The advice I can give to someone who is about to do the same exercise and interview a colleague who is about to leave is to take the default position of ‘he-or-she-knows-much-more-than-me’ rather than being judgemental on what you believe as the ‘truth’ or ‘reality’.
As many as we are coming from this global village, there is a great value in the diversity of perspectives and this is where I believe is the infinite source of innovation.
And of course, definitely check out those knowledge management tools on Paul’s shelf. They are really effective and surprisingly practical.
A comment from Paul
I have had the pleasure of mentoring ‘Jonny’ for the last couple of years during which time he has participated in board meetings, helped select a project management tool to act as store for the knowledge and documents on the various projects we’ve undertaken and conducted knowledge capture sessions. He is also the curator of our digital library.
I invted Jonny to be a guest contributor as I felt his experiences might be of value to others. Indeed his comments about the ‘give, get’ component of a knowledge capture process is particularly perceptive as often the drivers for such programmes are downsizing and layoffs where there is little positive feeling.
I am delighted he has contributed and would encourage you to join in with your comments.