The view from KM Asia 17
This was the first KM Asia event run by Ark Group I’ve attended in Hong Kong. Part of an Asian tour that also took in Kuala Lumpur and Singapore and comprised Masterclasses and presentations, I was there to give a talk on Collaborative Knowledge Spaces and run the hour long closing session styled thus:
KM competencies: A day in the life of a knowledge manager in 2020 “This highly interactive practical session will use a timeline technique to draw on the emerging themes of the conference. Paul will look at the skills likely to be required of a Knowledge & Information Manager in 2020. He will then invite delegates to imagine the life of a knowledge manager in 2020″
No pressure then!
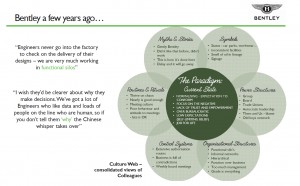
In prepping for the “future story” session I was indebted to Andrew Curry of Kantar Futures who I met to discuss one of the frameworks he uses to help clients imagine their future. Here’s how I used it in my presentation to paint a backdrop for the future.
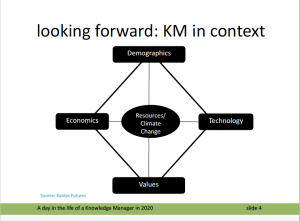 The backdrop:
The backdrop:
- The world’s working age population (especially in the developed world) is shrinking
- Big disruptive technology platforms emerge every 50-60 years or so. The current ICT (digital) wave is slowing down because the leading companies are no longer able to grow easily by adding more users; they need to find innovative ways to grow revenues per user, and this is challenging.
- Global growth is slowing: its a combination of demographics (how many people are working) and productivity (how much they are producing). Fewer people of working age means fewer people to support an aging population.
- Societal values are changing and the newest entrants to the workplace place less value on individual financial success and security, and more value on good work done for a good cause.
- Climate scientists suggest that by 2050, the average global temperature will have increased by anything between 0.8 and 2.8 degrees above levels in 1990. The implications for the world’s resources are significant and will in the shift to nationalism precipitate conflict.
So, what emerged from 2 very full and well attended days at the Royal Pacific Hotel Hong Kong and my closing session?
what surprised me?
- The group takeaways (3 highlights from each day) revealed how dfferently we see things and thru our own lenses.
- How few people had focused on the idea of curation being a role that the “Knowledgeur” (Knowledge Manager of the future?) might be required to fullfill.
- That one organisation who focuses on inspecting others did not have a process for feeding process enhancements and learnings back into their own.
what intrigued me?
- That those who’ve offshored functions are looking to bring them back in house as they now recognise the danger of critical knowledge loss.
- That the chat bots being used for basic ‘stuff’ cannot handle difficult complaints which are then passed over for human intervention.
- The thirst for accreditation: people and organisations want recognition for their knowledge and a KIM career path.
- That Hong Kong is still going through a massive building boom fuelled by demand from the mainland.
what delighted me?
 Rudolf D’Souza’s opening exercise with ‘Knowledge’ money
Rudolf D’Souza’s opening exercise with ‘Knowledge’ money- Three of the best presentations I’ve seen at a KM event on morning of Day Two from Eric Chan, Vincent Ribiere and Rudolf D’Souza. Set the bar high for my closing session!
- Meeting up with a former client and friend Olivier Serrat (formerly of ADB).
- The response to the closing session. Forget the scoring (6.4/7) and the nice feedback comments, the big plus was the enthusiastic way the delegates engaged with the exercise and were willing to ‘grab the mike’ at the end to tell the story of why their team had won a 2020 KM Award. More on that below.
what frustrated me?
- That few knowledge partnerships deliver according to Olivier Serrat. The majority of time is spent sharing news about the partnership.
- Jet lag: despite getting to Hong Kong early I was still tired from lack of sleep 5 days into the triip.
- That the ‘facilities’ were on another floor accessed by stairs and quite prescriptive in their use!
what was missing?
- Representation from the 3rd sector many of whom practice Knowledge & Information Management on a shoestring yet have developed some of the most effective tools and techniques.
quotes I took away:
Km has gone thru peak of inflated expectations which AI is now going thru (Les Hales)
Every company should have an anti strategy (Dave Aron)
Explore, Learn, Share, Ask, Incubate! (Ricky Tsui)
Technology should support not lead, it can’t understand rituals of people (Rudolf D’Souza)
and finally: what the delegates took away?
 As part of the closing session I asked delegates to get into groups of 5-6 with people they had not met during the event. I invited them to then reflect as individuals on the 3 “takeaways” they had from the morning and afternoon on both days.
As part of the closing session I asked delegates to get into groups of 5-6 with people they had not met during the event. I invited them to then reflect as individuals on the 3 “takeaways” they had from the morning and afternoon on both days.
Though simple it none the less brought to the surface ‘stuff’ or presentations that had made an impact. I further invited them as a group to consolidate their own findings.
And when that was complete to circle the room and see what others had noticed.
It proved to be an entertaining as well as an insightful session.
Looking forward to 2020 was the last exercise of the event. Having drawn on Kantar Futures research and brought to life my thoughts on the future role of the “Knowledgeur” (KIM’er of 2020) I asked the groups to imagine they were the recipients of an award and to describe what they had done to win it!
The ‘stories’ were brilliant and this (with grateful thanks to Nick Stone who captured the recording) was one of the best: KM Asia 17: KM in 2020 Future Story
If you want more on the event I was among a number who provided regular tweets and those can be found here: KM Asia 17 Twitter Stream



 January in Amsterdam has become a bit of a tradition as is leading the opening session at KM Legal Europe.
January in Amsterdam has become a bit of a tradition as is leading the opening session at KM Legal Europe.